This article mainly explains and analyzes the structural design characteristics of the sprocket based on its role in the scraper conveyor, thereby leading to the necessity of researching the material and processing technology of the sprocket and the key technical issues involved.
The Working Principle of the Scraper Sprocket
The sprocket is a key component for power drive in the scraper conveyor. The power of the motor is transmitted through the sprocket shaft to drive the sprocket, and the sprocket then drives the chain to transfer the power to the scraper. Thus, the scraper in the middle trough can drive the transportation of coal. As shown in the following figure, during the operation of the scraper sprocket, the chain meshed with it. Each chain is composed of two types: the flat chain link (simply referred to as the flat link) and the vertical chain link (simply referred to as the vertical link). Among them, the flat ring meshes with the chain socket of the sprocket, and the vertical ring is in the tooth groove of the sprocket. The contact between the flat ring and the chain socket drives the sprocket to rotate, and the sprocket drives the entire chain to rotate, thereby completing the work of the scraper conveyor. Therefore, the working performance of the sprocket mainly depends on the degree of contact and fit between the chain and the chain socket of the sprocket during use. The higher the degree of fit, the better the operational performance, and the longer the overall service life of the sprocket.
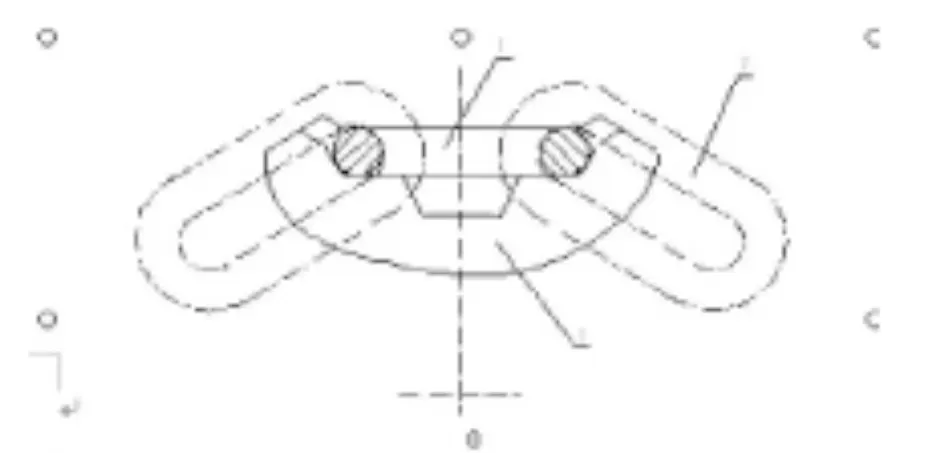
Design Structure Diagram of the Scraper Sprocket
According to the functional characteristics and structural processability of the scraper sprocket in the head and tail transmission parts of the conveyor, the design structure diagram of the sprocket is shown in the figure.
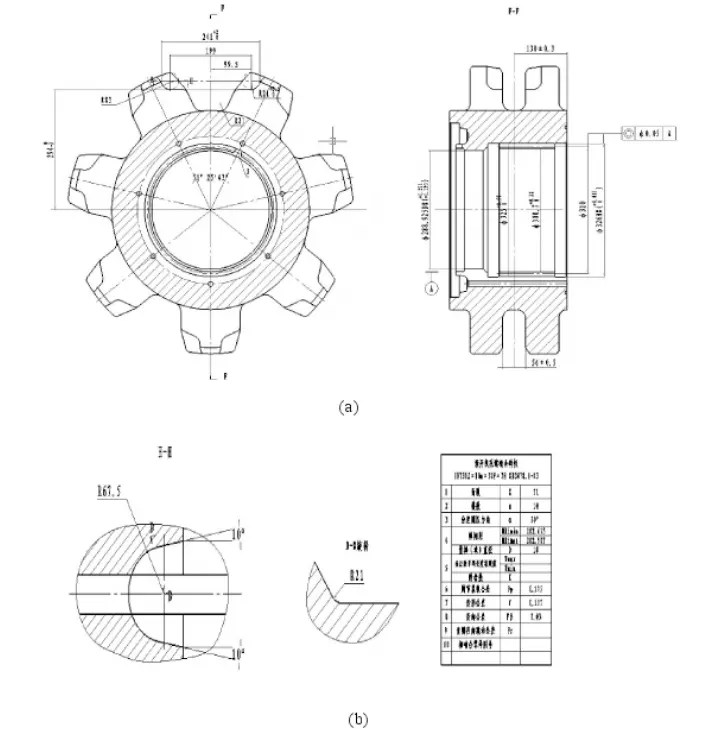
Key Dimensions of the Sprocket Chain Socket Part
According to the working principle of the sprocket, during the operation of the scraper sprocket, the parts that mesh with the chain are the key parts of the sprocket. The design of the sprocket chain hole dimensions is all in accordance with the coal industry standard MT231-91 “Drive Sprocket for Mine Scraper Conveyors”, and its main dimensions are shown in the following figure.
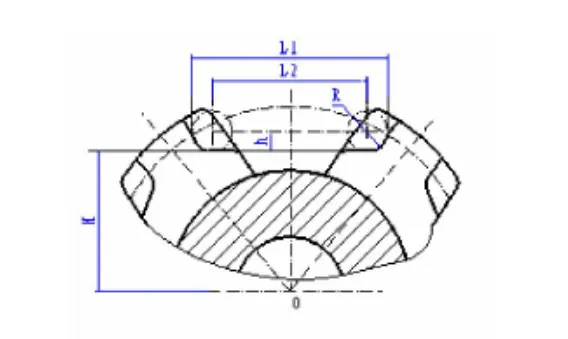
(1)The dimension H from the bottom plane of the chain socket to the center of the sprocket
This dimension is the installation dimension and has very strict requirements. During processing, it must be carried out in accordance with the requirements of the drawing. It is related to the meshing performance of the chain with the scraper sprocket during use, and has a direct impact on the service life of the sprocket. At the same time, it directly affects the meshing performance of the scraper sprocket and the chain. If it is too large, it will cause the depth dimension h to decrease, resulting in the chain slipping. If it is too small, it will cause the h size to increase, resulting in the chain getting stuck.
(2) The arc radius R of the chain socket
The radius of the chain groove arc is the size of a space, and the highest point is on the centerline of the two rows of tooth grooves. An arc is a spherical shape and cannot be directly measured with a caliper. The size of the arc radius R is the radius of the corresponding specification chain link. For example, the arc radius of the chain socket corresponding to a φ48 round link chain is R24. During the working process, the chain link comes into contact with this part. Therefore, when processing, it is necessary to ensure the surface quality of this part to achieve good fit between the chain link and this part.
(3) The length L of the chain socket
L1 is the distance between the intersection points of the bottom arcs and the pitch circles of two adjacent toothed chain slots, which is the maximum length of the chain slot. L2 is the effective length at the center of the chain slot. When a circular link chain is placed in a formed chain socket, the link can move flexibly left and right within the socket. The movement range is within L1, and the movement amount is generally 8mm in size. Under normal circumstances, the amount of movement plus the longest outer diameter of the chain link is equal to the maximum length L1 of the chain socket. The size of L1 cannot be directly measured with a caliper. However, it can be measured indirectly. L1=L2+φd+8, where d is the diameter of the chain link.
(4) The depth h of the chain socket
The depth of the chain socket is the distance from the center of the round link chain to the bottom plane of the chain socket. During processing, the main focus is on ensuring the size H from the center of the sprocket to the bottom surface of the chain socket, while also taking into account the depth size h of the chain socket. The depth size h of the chain socket is directly guaranteed by the forming milling cutter.
The Basic Technical Requirements for Sprockets
All the sprockets studied in the paper comply with the technical requirements of MT231-91. The deviation of the centerline angles of adjacent two chain grooves is no more than ±30. The flatness of the bottom surface of the chain groove flat ring is no more than 1. The quenching and tempering hardness of the sprocket is HB255-285, and the quenching hardness of the sprocket tooth surface is HRC48-58. The depth of the hardened layer shall not be less than 10mm, and the offset between the centerline J of the involute spline tooth profile and the centerline M of the sprocket reference shall not exceed 15 ‘. Mark “▽” equilateral triangles with a side length of 8mm on both sides of the reference tooth M at the positions shown in the figure.

Summary
This article mainly explains and analyzes the structural design features and basic technical requirements of the sprocket from the perspective of its role and working principle in the scraper conveyor. In this way, it can provide a certain theoretical basis for the necessity of the next step of research on the material selection and processing technology of the sprocket and the key technical issues involved.
