Opis produktu
1. Produce strictly in accordance with standard dimension
2. Material: 1045 Steel / Alloy Steel / Stainless Steel 304 & 316
3. Standard: ANSI, DIN, JINS, ISO, KANA,Standard America or customer's drawing
4. Pilot bore, finished bore, taper bore and special bore.
5. Bright surface / high precision / Blacking /Electrophoretic-Coated
6. Advanced heat treatment and surface treatment craft
7. Best quality and competitive price.
8. Welcome OEM / ODM
9. Processing Equipment: Hobbing machine, Slotting machine, CNC lathes and other equipment.
10. Sprocket Models: Contains special sprocket according to customer's drawings, standard s
Haodan Transmission Parts Co., LTD., located in ZheJiang HangZhou HangZhou beautiful Baiyangdian Xiongan New Area, HangZhou is a famous sprocket town in China, a variety of mechanical parts production, 90% of the country's sprockets from HangZhou Xihu (West Lake) Dis.qiao Town exports and heavy countries, for a number of countries have made contributions to the production of machinery. Haotan Transmission Parts Co., Ltd. has more than 30 years of production experience, 2 generations of efforts by a small workshop slowly set up a limited company, in line with the quality of survival, to win the price of customers, to the business philosophy of faith and development to serve our customers, so that customers first, quality first.
procket (American standard and metric). /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
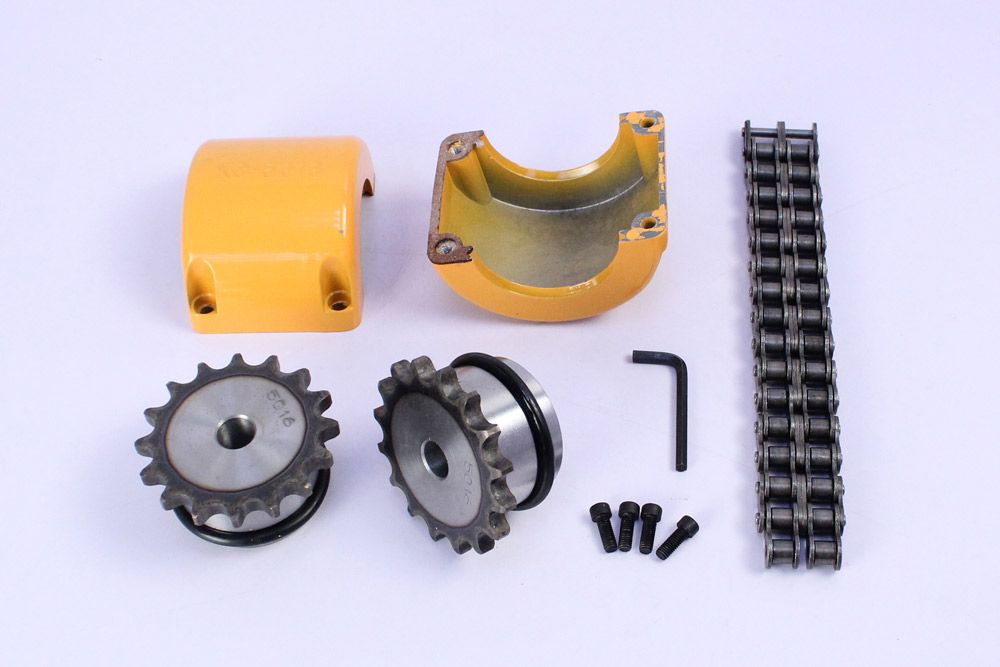
What are the common materials used in chain couplings?
Chain couplings are commonly made from various materials that offer the necessary strength, durability, and wear resistance required for transmitting torque between shafts. The choice of materials depends on factors such as the application requirements, operating conditions, and the specific design of the coupling. Here are some common materials used in chain couplings:
- Steel: Steel is one of the most widely used materials for chain couplings. It offers excellent strength, toughness, and resistance to wear and fatigue. Carbon steel and alloy steel are commonly used, with alloy steel providing enhanced properties such as higher tensile strength and improved corrosion resistance.
- Stainless Steel: Stainless steel is chosen for chain couplings when corrosion resistance is a critical requirement. It offers good mechanical properties along with resistance to rust and corrosion, making it suitable for applications in harsh environments or where exposure to moisture or chemicals is present.
- Cast Iron: Cast iron is occasionally used for chain couplings, particularly in applications where cost-effectiveness and moderate strength are important factors. Cast iron provides good wear resistance and can withstand moderate loads and operating conditions.
- Bronze: Bronze is utilized in certain specialized chain couplings, especially in applications where self-lubrication and high resistance to corrosion are required. Bronze has good friction properties and can operate in conditions where lubrication may be limited or unavailable.
- Plastics: In some cases, certain plastics, such as nylon or polyurethane, are used for chain coupling components like chain guides or protective covers. Plastics offer low friction, noise reduction, and resistance to chemicals, making them suitable for specific applications.
It's important to note that the materials used in chain couplings may vary depending on the specific manufacturer, coupling design, and application requirements. It is recommended to consult the manufacturer's specifications and guidelines to determine the appropriate materials for a particular chain coupling.
Additionally, in some cases, chain couplings may incorporate a combination of different materials, such as steel for the sprockets and roller chain, and elastomers for the flexible elements. This hybrid construction allows for optimized performance, balancing strength, flexibility, and damping characteristics.
Overall, the selection of materials for chain couplings is crucial to ensure reliable and efficient power transmission while considering factors such as load capacity, operating conditions, and the desired service life of the coupling.

How does misalignment affect chain couplings?
Misalignment in chain couplings can have detrimental effects on their performance and lifespan. Here are some ways in which misalignment can affect chain couplings:
- Increase in Load: Misalignment puts additional load on the coupling components. When the shafts connected by the coupling are not properly aligned, the coupling must compensate for the angular, parallel, or axial misalignment. This increased load can lead to excessive stress and premature wear on the coupling components, such as sprockets, roller chain, and connecting pins.
- Uneven Load Distribution: Misalignment can cause an uneven distribution of load across the coupling. As a result, some sections of the coupling experience higher stresses than others. This uneven load distribution can lead to localized wear and fatigue, reducing the overall strength and reliability of the coupling.
- Reduced Power Transmission: Misalignment affects the efficiency of power transmission through the coupling. When the shafts are not properly aligned, there is increased friction and slippage between the roller chain and the sprockets. This slippage reduces the amount of power transferred from one shaft to another, resulting in a loss of efficiency and a decrease in the overall performance of the machinery or equipment.
- Increased Wear: Misalignment can accelerate wear on the coupling components. The misalignment causes the roller chain to operate at an angle or with excessive tension, causing additional stress and wear on the chain links, sprocket teeth, and connecting pins. The increased wear can lead to chain elongation, loss of engagement with the sprockets, and ultimately, coupling failure.
- Hałas i wibracje: Misalignment often results in increased noise and vibration during operation. The misaligned coupling generates additional vibrations and impacts, leading to excessive noise and potential damage to the coupling and surrounding equipment. These vibrations can also propagate through the connected machinery, affecting its overall performance and reliability.
To mitigate the negative effects of misalignment, it is crucial to ensure proper alignment of the shafts and the chain coupling during installation and periodically check and adjust the alignment as needed. Proper alignment minimizes stress on the coupling components, maximizes power transmission efficiency, and extends the service life of the chain coupling.

Jakie są dostępne rodzaje sprzęgieł łańcuchowych?
Sprzęgła łańcuchowe występują w różnych wzorach i konfiguracjach, aby spełnić różne wymagania aplikacji. Oto kilka typowych typów sprzęgieł łańcuchowych:
- Standardowe sprzęgła łańcuchowe rolkowe: Są to najbardziej podstawowe i powszechnie stosowane rodzaje sprzęgieł łańcuchowych. Składają się z dwóch zębatek połączonych łańcuchem rolkowym. Zębatki mają hartowane zęby, które zazębiają się z rolkami łańcucha, zapewniając niezawodną transmisję mocy. Standardowe sprzęgła łańcuchowe rolkowe są na ogół odpowiednie do zastosowań o umiarkowanych wymaganiach dotyczących momentu obrotowego i prędkości.
- Podwójne sprzęgła łańcuchowe rolkowe: Double roller chain couplings are similar to standard roller chain couplings but feature two parallel roller chains instead of one. This design increases the torque capacity and allows for higher power transmission. Double roller chain couplings are often used in applications that require higher torque and increased load-bearing capabilities.
- Sprzęgła łańcuchowe ciche: Ciche sprzęgła łańcuchowe, znane również jako sprzęgła łańcuchowe z odwróconymi zębami, wykorzystują specjalny łańcuch zębaty z zazębiającą się konstrukcją zębatki. Zęby łańcucha zazębiają się z rowkami zębatki, zapewniając płynną i cichą pracę. Ciche sprzęgła łańcuchowe są powszechnie stosowane w zastosowaniach, w których ważna jest redukcja hałasu, takich jak precyzyjne maszyny lub urządzenia pracujące w środowiskach wrażliwych na hałas.
- Sprzęgła łańcuchowe o dużej wytrzymałości: Sprzęgła łańcuchowe o dużej wytrzymałości są przeznaczone do zastosowań wymagających solidnej i wytrzymałej wydajności. Są zbudowane z większych zębatek i wytrzymałych łańcuchów rolkowych, aby obsługiwać wysoki moment obrotowy i duże obciążenia. Sprzęgła te są powszechnie stosowane w takich gałęziach przemysłu, jak górnictwo, produkcja stali i papieru, gdzie występują ekstremalne warunki pracy i ciężki sprzęt.
- Elastyczne sprzęgła łańcuchowe: Elastyczne sprzęgła łańcuchowe zawierają element elastomerowy, taki jak wkładka gumowa lub poliuretanowa, pomiędzy zębatkami a łańcuchem. Ten element zapewnia elastyczność, tłumienie i pewien stopień kompensacji odchylenia. Elastyczne sprzęgła łańcuchowe nadają się do zastosowań wymagających amortyzacji wstrząsów, tłumienia drgań i umiarkowanej tolerancji odchylenia.
- Sprzęgła łańcuchowe ze stali nierdzewnej: Sprzęgła łańcuchowe ze stali nierdzewnej są specjalnie zaprojektowane do zastosowań wymagających odporności na korozję i higieny, takich jak przetwórstwo żywności, przemysł farmaceutyczny i chemiczny. Wykonane są ze stali nierdzewnej lub innych materiałów niekorodujących, aby wytrzymać trudne warunki i utrzymać higieniczne warunki.
To tylko kilka przykładów różnych typów dostępnych sprzęgieł łańcuchowych. Każdy typ ma swoje zalety i jest odpowiedni do konkretnych wymagań aplikacji. Ważne jest, aby dokładnie rozważyć moment obrotowy, prędkość, rozbieżność, czynniki środowiskowe i inne specyficzne dla aplikacji potrzeby przy wyborze odpowiedniego typu sprzęgła łańcuchowego do konkretnego zastosowania.


editor by CX 2024-03-06
