Opis produktu
Advantages of Belt pulley:
(1) Pulley drive can mitigate the impact of load;
(2) Belt pulley drive running smoothly, low noise, low vibration;
(3) Belt pulley transmission structure is simple, easy to adjust;
(4) pulley manufacturing and installation precision is not as strict as meshing transmission;
(5) Belt pulley transmission has the function of overload protection;
(6) Belt pulley transmission of the 2 axis center distance adjustment range is large.
European standard pulley installation:
1. check the groove of the belt pulley according to the European standard to ensure that there is no scar or edge.
All sizes meet the standard;
2. Clean the surface of all parts of euro standard pulley, and manufacturers of euro standard pulley, such as hub hole, cone
sleeve, bolt hole, etc.Fit the cone set into the pulley so that all the screw holes are aligned.
3. Apply oil on the screw rod and thread of European standard pulley and then screw it into the mounting hole, but do not tighten
it for the time being.
4. Clean the surface of the European standard belt pulley drive shaft, push the belt pulley with cone sleeve to the predetermined
position on the shaft, and check whether the triangle belt pulley is aligned.
5. When using the European standard belt pulley keyway, it must be inserted into the hub first. There must be a certain tolerance
between the keyway and the hole hub.
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Orzecznictwo: | ISO |
|---|---|
| Rozmiary kół pasowych: | Type B |
| Proces produkcyjny: | Odlew |
| Tworzywo: | Carbon Steel |
| Surface Treatment: | Oxygenation |
| Aplikacja: | Chemical Industry, Grain Transport, Mining Transport, Power Plant |
| Próbki: |
US$ 1500/Piece
1 sztuka (minimalne zamówienie) | |
|---|
| Personalizacja: |
Dostępny
| Spersonalizowane żądanie |
|---|
What is the difference between a fixed and a swivel pulley?
Fixed and swivel pulleys are two common types of pulleys that differ in their design and functionality. Here are the key differences between these two types:
1. Fixed Pulley: A fixed pulley is a type of pulley that is mounted or attached to a fixed point, such as a beam or a ceiling. It does not move or rotate independently of its mounting point. The primary function of a fixed pulley is to change the direction of the force applied to a rope or cable. When a force is applied to the rope or cable passing through a fixed pulley, the load moves in the opposite direction. However, a fixed pulley does not provide any mechanical advantage, meaning it does not reduce the effort required to lift the load.
2. Swivel Pulley: A swivel pulley, also known as a movable pulley, is designed to rotate or swivel on a separate mounting point. It has a built-in mechanism that allows it to move independently. Unlike a fixed pulley, a swivel pulley is capable of changing both the direction and the magnitude of the force applied to the rope or cable. When a force is applied to the rope or cable passing through a swivel pulley, the load moves in the same direction as the applied force. Additionally, a swivel pulley provides a mechanical advantage by distributing the load's weight over multiple strands of rope or cable, reducing the effort required to lift the load.
In summary, the main differences between fixed and swivel pulleys are:
– Fixed pulleys are stationary and do not move independently, while swivel pulleys can rotate or swivel on a separate mounting point.
– Fixed pulleys change the direction of the force applied to the rope or cable, while swivel pulleys change both the direction and the magnitude of the force.
– Fixed pulleys do not provide a mechanical advantage, while swivel pulleys provide a mechanical advantage by distributing the load's weight over multiple strands of rope or cable.
Both fixed and swivel pulleys have their specific applications and can be used individually or in combination with each other to achieve desired mechanical functions in various systems and setups.

How do pulleys contribute to the functioning of bicycles and motorcycles?
Pulleys play important roles in the functioning of both bicycles and motorcycles, aiding in power transmission, speed control, and overall mechanical efficiency. Here's how pulleys contribute to the operation of these vehicles:
1. Bicycles:
– Derailleur System: In most modern bicycles, pulleys are used in the derailleur system. The derailleur is responsible for shifting the bicycle chain between different gears on the front and rear sprockets. Pulleys, often referred to as jockey wheels, are positioned in the derailleur to guide and tension the chain as it moves between gears. They ensure smooth and precise shifting, allowing the rider to adapt to various terrains and maintain an optimal pedaling cadence.
– Belt Drive Systems: Some bicycles use a belt drive instead of a traditional chain drive. Belt drives employ a pulley system that consists of a front pulley attached to the pedal crank and a rear pulley attached to the rear wheel hub. The belt is wrapped around these pulleys, transferring power from the rider's pedaling motion to propel the bicycle forward. Pulleys in belt drive systems enable efficient power transfer, reduce maintenance needs, and provide a quieter and cleaner alternative to chain drives.
2. Motorcycles:
– Clutch System: Pulleys, known as clutch pulleys, are utilized in motorcycle clutch systems. The clutch connects the engine to the transmission and allows the rider to engage or disengage power transmission to the rear wheel. When the clutch lever is pulled, the clutch pulley separates the engine's rotational motion from the transmission, disengaging power transfer. Releasing the clutch lever brings the pulley back into contact, engaging power transmission and enabling the motorcycle to move.
– Variable Transmission Systems: Some motorcycles employ pulleys in variable transmission systems, such as continuously variable transmissions (CVT). CVTs use a pair of pulleys connected by a belt or chain. By changing the diameter of the pulleys, the CVT adjusts the gear ratio continuously, providing seamless and efficient power delivery across a wide range of speeds. Pulleys in variable transmission systems contribute to smooth acceleration, improved fuel efficiency, and enhanced riding comfort.
– Drive Belt Systems: Pulleys are also utilized in motorcycles equipped with belt drive systems. Similar to bicycles, these systems consist of a front pulley connected to the engine's crankshaft and a rear pulley connected to the rear wheel. The belt runs around these pulleys, transferring power from the engine to the rear wheel. Belt drive systems offer advantages such as reduced maintenance, quieter operation, and smoother power delivery compared to traditional chain drives.
Overall, pulleys are integral components in bicycles and motorcycles, contributing to smooth gear shifting, efficient power transmission, and improved overall performance. Whether in derailleur systems, belt drive systems, clutch systems, or variable transmission systems, pulleys play a vital role in enhancing the functionality and ride experience of these vehicles.
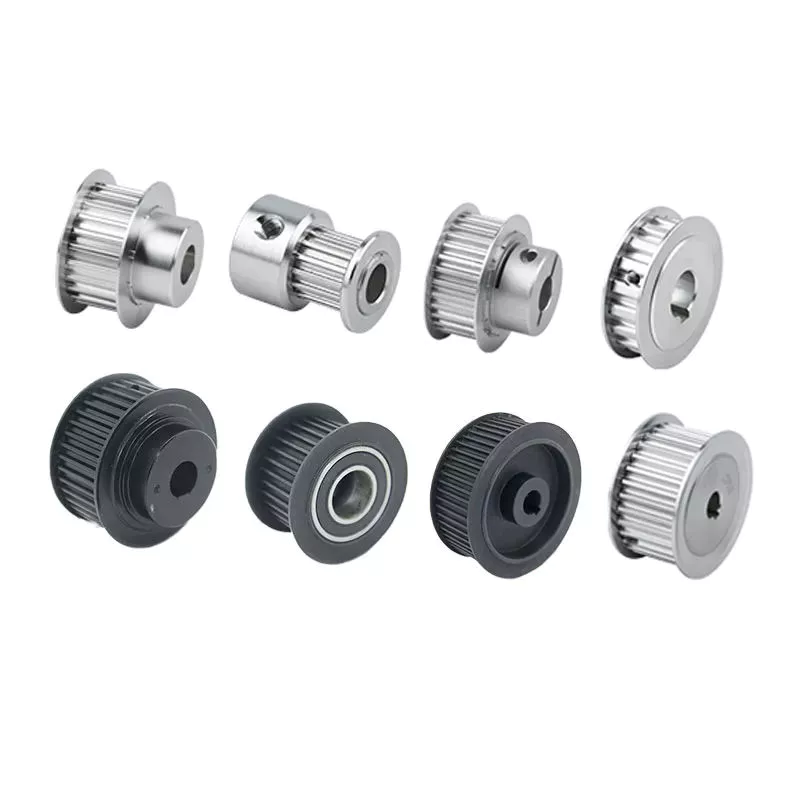

Czy koła pasowe można dostosować do konkretnych zastosowań?
Tak, koła pasowe można dostosować do konkretnych wymagań różnych zastosowań. Dostosowanie umożliwia dostosowanie kół pasowych do konkretnych rozmiarów, kształtów, materiałów i charakterystyk wydajności. Oto szczegółowe wyjaśnienie, w jaki sposób koła pasowe można dostosować:
1. Rozmiar i kształt: Koła pasowe można dostosować pod względem rozmiaru i kształtu, aby pasowały do konkretnych ograniczeń przestrzennych i układu zastosowania. Obejmuje to zmiany średnicy, szerokości, konfiguracji rowków i ogólnej konstrukcji. Niestandardowe rozmiary i kształty zapewniają optymalne dopasowanie i kompatybilność w systemie, umożliwiając wydajny i efektywny rozkład obciążenia i podnoszenie.
2. Materiały: Koła pasowe można dostosować na podstawie materiałów użytych do ich budowy. Różne materiały oferują różne właściwości, takie jak wytrzymałość, trwałość, waga i odporność na korozję lub zużycie. Wybierając odpowiednie materiały, koła pasowe można dostosować do konkretnych warunków pracy danego zastosowania, w tym temperatury, wilgotności i narażenia na działanie chemikaliów lub trudnych warunków środowiskowych.
3. Systemy łożyskowe: System łożysk koła pasowego można dostosować do wymagań aplikacji. Różne typy łożysk, takie jak łożyska kulkowe lub łożyska wałeczkowe, można wybrać na podstawie czynników takich jak nośność, prędkość obrotowa i pożądane charakterystyki tarcia. Dostosowanie systemu łożyskowego zapewnia płynny obrót, zmniejszone tarcie i ulepszoną ogólną wydajność koła pasowego.
4. Powłoki i obróbka powierzchni: Koła pasowe mogą być dostosowane do różnych powłok i obróbek powierzchni w celu zwiększenia wydajności. Na przykład koła pasowe używane w zastosowaniach, w których występują wysokie temperatury, mogą skorzystać z powłok odpornych na ciepło. Koła pasowe używane w środowiskach z substancjami żrącymi mogą być pokryte materiałami ochronnymi w celu zapobiegania korozji. Obróbki powierzchni, takie jak polerowanie lub powlekanie, mogą być również stosowane w celu zmniejszenia tarcia, poprawy odporności na zużycie lub zapewnienia określonych właściwości powierzchni.
5. Nośność i wydajność: Koła pasowe można dostosować do konkretnych wymagań dotyczących nośności i wydajności. Obejmuje to określenie liczby kół pasowych w systemie, wybór odpowiednich współczynników kół pasowych i skonfigurowanie układu kół pasowych w celu uzyskania pożądanej przewagi mechanicznej. Dostosowanie umożliwia optymalizację kół pasowych pod kątem konkretnych wymagań dotyczących obciążenia, zapewniając efektywny rozkład obciążenia i podnoszenie.
6. Integracja z systemami: Koła pasowe można dostosować, aby bezproblemowo zintegrować je z istniejącymi systemami lub urządzeniami. Obejmuje to projektowanie kół pasowych z kompatybilnymi interfejsami, opcjami montażu i metodami łączenia. Dostosowanie zapewnia prawidłowe wyrównanie, łatwą instalację i płynne działanie podczas włączania kół pasowych do całego systemu.
7. Zastosowania specjalistyczne: W niektórych specjalistycznych zastosowaniach koła pasowe można dostosować do wyjątkowych wymagań. Może to obejmować projektowanie kół pasowych do ekstremalnych warunków pracy, takich jak wysokie prędkości lub duże obciążenia, lub opracowywanie kół pasowych ze szczególnymi cechami, takimi jak wbudowane czujniki lub mechanizmy blokujące. Dostosowywanie umożliwia dostosowanie kół pasowych do konkretnych potrzeb niszowych zastosowań.
Dostosowywanie kół pasowych jest zazwyczaj wykonywane przez producentów lub dostawców, którzy mają wiedzę specjalistyczną i możliwości projektowania i produkcji kół pasowych zgodnie ze szczegółowymi wymaganiami klienta. Pozwala to na optymalizację wydajności kół pasowych, kompatybilności i wydajności w szerokim zakresie zastosowań.


redaktor przez CX
2024-01-19
