Opis produktu
Opis produktu:
Product Name: Sliding Roller HN-1035-9
Dimensions: ID=10mm; OD=35mm; Height=9mm
Outside Material: Polyformaldehyde (POM), Polyamide(PA6, PA66, Nylon), Polypropylene(PP), Polycarbonate(PC), Polyurethane(PU)
Insert Material: Carbon Steel, Chrome Steel, Stainless Steel
Color: All colors available
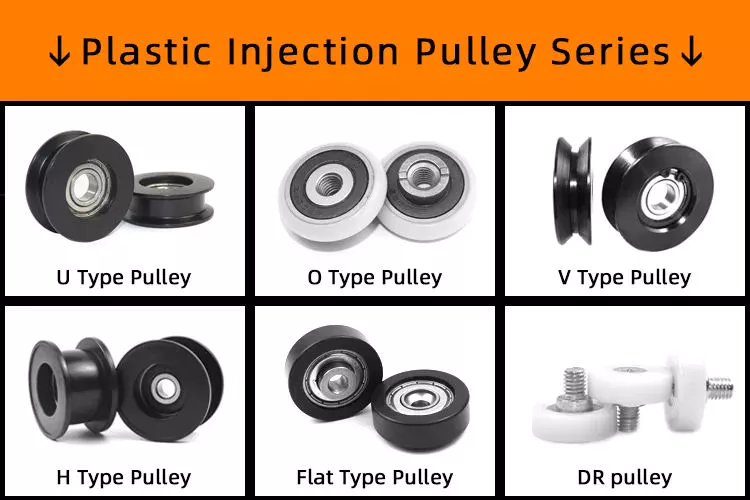
Profile Type:V Groove
Surface Treatment: Lathing
Structure: HN-625ZZ(ID=10mm, OD=35mm, Width=9mm)bearing injected with POM
Service: OEM&ODM
Experience: With 15 years manufacturing history
Adventage:
1) Built-in precise micro bearing;
2) Low noise, elegant performance and rolling smoothly;
3) Superior in quality and moderate in price;
4) We can supply both standard products and customized items according to the customers’ special requirements.
5) We can provide free samples for your reference.
Payment & Packaging &Delivery:
Warunki płatności:
1) 100% T/T
2) 30% T/T in advance, 70% against copy of BL
3) Paypal
Packaging Details: Standard export packing (Plastic bag, cartons and pallets or wooden case);
As customers’ requirement
Delivery Port: HangZhou / ZheJiang
Delivery Time: Normally ready goods and stock within 30 days or as the customer’s request
PS: 1) material and color can according to customers’ requirement.
2) we can make different size as per customers’ requirement.
Często zadawane pytania
Q: Are you the manufacturer?
A: Yes, we are a professional manufacturer focused on door and window roller pulleys for over 15 years.
Q: Do you offer free samples?
A: Yes, we are very glad to offer free samples for you to check the quality.
Q: Can we make our own color box?
A: Yes, if the order quantity reaches 1000 sets, we can make a customized color box for you.
Q: Can we print our logo on the products?
A: Yes, we can print your logo on the products according to your design.
Q: How does your factory do regarding quality control?
A: 80% of the staff has 10 years experience, a mature skilled technical team, and a complete quality management system to ensure high quality.
Q: What is the after-sale service for the sliding rollers?
A: We have online technical support. If it is a quality problem, we will replace the broken ones with new ones.
Q: How long is the production time?
A: For samples in stock, shipped in 2 days. if not in stock, the lead time is in 7 days. For mass production, the lead time is around 15 days after receiving the deposit payment.
Q: How about the shipment?
A: For small orders, we can ship them by DHL, FedEx, UPS, TNT, etc. For mass production orders, we can ship them by sea or by air. /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Kąt kontaktu: | / |
|---|---|
| Justowanie: | Łożysko |
| Rozdzielony: | Unseparated |
| Load Direction: | Radial Bearing |
| Tworzywo: | Nylon/Plastic/POM |
| Cechy: | Work Smoothly,Low Noise,Widely Use,Standard,Custo |
| Próbki: |
US$ 0/Piece
1 sztuka (minimalne zamówienie) | |
|---|
| Personalizacja: |
Dostępny
| Spersonalizowane żądanie |
|---|

What are the common problems and maintenance requirements for pulleys?
Pulleys, like any mechanical component, can experience common problems and require regular maintenance to ensure their proper functioning and longevity. Here are some of the common problems and maintenance requirements for pulleys:
1. Wear and Tear: Over time, pulleys can experience wear and tear due to friction, load stress, and environmental factors. This can result in issues such as worn grooves, cracked or deformed pulley bodies, or damaged bearings. Regular inspection is necessary to identify signs of wear and address them promptly.
2. Misalignment: Pulleys can become misaligned, causing the belt or rope to run off its intended path. This can lead to inefficient power transmission, increased wear on the belt, and reduced overall system performance. Regular alignment checks and adjustments are necessary to ensure proper alignment of pulleys and belts.
3. Belt Tension: Proper belt tension is crucial for optimal pulley performance. Over time, belts can stretch or become loose, resulting in inadequate tension. Insufficient tension can cause slippage, reduced power transfer, and premature wear. Regular checks and adjustments of belt tension are necessary to maintain optimal performance.
4. Contamination: Pulleys can accumulate dirt, dust, debris, or other contaminants, particularly in industrial or outdoor environments. Contamination can lead to increased friction, reduced efficiency, and accelerated wear. Regular cleaning of pulleys is necessary to prevent buildup and maintain smooth operation.
5. Lubrication: Pulleys with bearings require proper lubrication to minimize friction and ensure smooth rotation. Insufficient lubrication can lead to increased friction, heat generation, and premature bearing failure. Regular lubrication according to manufacturer recommendations is essential for optimal pulley performance and longevity.
6. Bearing Maintenance: Pulleys with bearings should undergo regular bearing maintenance. This includes inspecting bearings for signs of wear or damage, cleaning them, and replacing worn-out or faulty bearings. Proper bearing maintenance helps prevent bearing failure, which can lead to pulley malfunction or system downtime.
7. Environmental Factors: Pulleys used in outdoor or harsh environments may be exposed to adverse conditions such as extreme temperatures, moisture, chemicals, or corrosive substances. Extra care should be taken to protect pulleys from these environmental factors. This may involve using appropriate seals, covers, or coatings and implementing preventive measures to mitigate the effects of the environment.
8. Regular Inspections: Regular inspections are crucial for identifying potential problems early on. Inspect pulleys for signs of wear, damage, misalignment, or other issues. Address any identified problems promptly to prevent further damage or system failure.
9. Replacement of Worn-out Parts: If any components of the pulley, such as the belt, bearings, or fasteners, are worn out or damaged beyond repair, they should be replaced promptly. Using worn-out parts can compromise the performance and safety of the pulley system.
10. Manufacturer Guidelines: Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for maintenance and servicing of pulleys. Manufacturers often provide specific instructions on maintenance intervals, lubrication requirements, and other important considerations.
By proactively addressing these common problems and adhering to regular maintenance requirements, pulley performance and service life can be optimized, ensuring smooth and reliable operation in various applications.
Czy bloczki można stosować do podnoszenia zarówno w poziomie, jak i w pionie?
Yes, pulleys can be used for both horizontal and vertical lifting. The versatility of pulley systems allows them to be utilized in various lifting applications, regardless of the direction of the load. Here’s how pulleys can be used for horizontal and vertical lifting:
1. Podnoszenie poziome: W scenariuszach podnoszenia poziomego, koła pasowe mogą być używane do zmiany kierunku siły przyłożonej do ładunku. Poprzez użycie kombinacji stałych i ruchomych kół pasowych, siła może zostać przekierowana, aby ciągnąć ładunek poziomo. Jest to powszechnie widoczne w zastosowaniach, takich jak ręczne podnośniki lub systemy bloków i wciągników stosowane w budownictwie, gdzie ciężkie przedmioty muszą być przenoszone poziomo na odległość.
2. Vertical Lifting: Pulleys are widely used in vertical lifting applications, such as cranes, elevators, and lifting systems. In these setups, the pulleys are typically arranged in such a way that the load can be lifted vertically. By using multiple pulleys and ropes or cables, mechanical advantage can be achieved, making lifting heavier loads easier. The pulleys distribute the load’s weight across multiple lines, reducing the effort required to lift the load.
It’s worth noting that the number and arrangement of pulleys can vary depending on the specific lifting requirements. For example, a single fixed pulley can change the direction of the force but does not provide any mechanical advantage. On the other hand, systems with multiple pulleys, such as compound pulley systems or block and tackle setups, can provide significant mechanical advantage, making lifting heavier loads more manageable.
Niezależnie od tego, czy jest to podnoszenie poziome czy pionowe, zasady mechaniki kół pasowych pozostają takie same. Koła pasowe umożliwiają przekierowanie siły, przewagę mechaniczną i rozkład obciążenia, dzięki czemu zadania związane z podnoszeniem są bardziej wydajne i łatwiejsze w zarządzaniu. Konkretna konfiguracja i ustawienie układu kół pasowych będzie zależeć od wymagań dotyczących podnoszenia i pożądanego poziomu przewagi mechanicznej.

Jakie rodzaje kół pasowych są powszechnie stosowane w przemyśle?
Koła pasowe są szeroko stosowane w różnych gałęziach przemysłu do różnych zastosowań. Oto różne rodzaje powszechnie stosowanych kół pasowych:
1. Stałe koła pasowe: Stałe koła pasowe są przymocowane do nieruchomej konstrukcji, takiej jak sufit lub ściana. Zmieniają kierunek siły przyłożonej bez zapewniania żadnej przewagi mechanicznej. Stałe koła pasowe są często używane w połączeniu z innymi kołami pasowymi w celu tworzenia bardziej złożonych systemów.
2. Ruchome bloczki: Ruchome bloczki są przymocowane do ładunku, który jest przenoszony, i poruszają się wraz z nim. Te bloczki zapewniają przewagę mechaniczną, zmniejszając wysiłek wymagany do podniesienia ładunku. Ruchome bloczki są powszechnie stosowane w systemach, takich jak układy bloków i wciągników, do podnoszenia ciężkich przedmiotów z mniejszą siłą.
3. Koła pasowe złożone: Koła pasowe złożone składają się z kombinacji kół stałych i ruchomych. Zapewniają większą przewagę mechaniczną niż pojedyncze koło pasowe, rozkładając obciążenie na wiele segmentów liny lub pasa. Systemy kół pasowych złożonych są często stosowane w zastosowaniach wymagających podnoszenia wyjątkowo ciężkich ładunków.
4. Bloki snatch: Bloki snatch to bloczki z płytą boczną, którą można otworzyć, aby włożyć lub wyjąć linę lub kabel bez przewlekania ich przez bloczek. Są powszechnie stosowane w zastosowaniach związanych z olinowaniem i holowaniem, aby zmienić kierunek siły i uzyskać przewagę mechaniczną.
5. Koła pasowe paska klinowego: Koła pasowe paska klinowego mają rowek w kształcie litery V, który pasuje do przekroju poprzecznego paska klinowego. Są stosowane w układach napędowych pasowych do przenoszenia mocy między dwoma wałami. Koła pasowe paska klinowego są powszechnie stosowane w takich zastosowaniach, jak maszyny przemysłowe, silniki samochodowe i systemy HVAC.
6. Koła pasowe rozrządu: Koła pasowe rozrządu mają zęby, które zazębiają się z zębami paska rozrządu. Są stosowane w układach napędowych synchronicznych w celu zapewnienia dokładnego i zsynchronizowanego przenoszenia mocy. Koła pasowe rozrządu są powszechnie stosowane w takich zastosowaniach jak robotyka, prasy drukarskie i maszyny CNC.
7. Krążki linowe: Krążki linowe mają gładką powierzchnię zaprojektowaną w celu zminimalizowania tarcia i zapobiegania zużyciu lin. Są powszechnie stosowane w zastosowaniach, w których liny są używane do podnoszenia lub ciągnięcia, takich jak dźwigi, windy i sprzęt do transportu materiałów.
8. Krążki linowe: Krążki linowe są specjalnie zaprojektowane do stosowania z linami stalowymi. Mają rowki lub kieszenie, które dostosowują się do kształtu i rozmiaru lin stalowych, zapewniając pewny chwyt i skuteczną transmisję siły. Krążki linowe są powszechnie stosowane w takich zastosowaniach, jak dźwigi, wciągarki i podnośniki.
9. Koła pasowe napinające: Koła pasowe napinające służą do prowadzenia i napinania pasów lub lin w systemie. Nie przenoszą mocy, ale pomagają utrzymać właściwe naprężenie i wyrównanie pasów. Koła pasowe napinające są powszechnie stosowane w systemach przenośników, silnikach samochodowych i innych zastosowaniach napędzanych pasem.
10. Koła pasowe: Koła pasowe to duże koła pasowe stosowane w ciężkich zastosowaniach, takich jak systemy dźwigowe i windy. Są zaprojektowane do obsługi dużych obciążeń i zapewniają płynną i niezawodną pracę. Koła pasowe często mają wiele rowków, aby pomieścić wiele lin lub pasów.
Oto niektóre z różnych typów kół pasowych powszechnie stosowanych w różnych branżach. Każdy typ ma określone cechy i jest wybierany na podstawie wymagań zastosowania, takich jak nośność, przenoszenie mocy i warunki pracy.


redaktor przez CX
2024-03-14
