Produktbeschreibung
Cummins Engine Part Idler Pulley 4991240/3978019/3935015 for CHINAMFG 6B5.9 Engine
DCEC engine part:
More CHINAMFG engine parts in sock:
| PNs | Parts Description_English | |||||||||||||||
| C2830346 | CONNECTION,WATER INLET | |||||||||||||||
| C2830405 | BREATHER,CRANKCASE | |||||||||||||||
| C2830409 | SEAL,O RING | |||||||||||||||
| C283571 | SCREW,HEX FLANGE HEAD CA | |||||||||||||||
| C283571 | SCREW,HEX FLANGE HEAD CA | |||||||||||||||
| C283 0571 | SEAL,O RING | |||||||||||||||
| C2831066 | COLLAR,SHAFT | |||||||||||||||
| C2831103 | SCREW,ROUND HEAD CAP | |||||||||||||||
| C2831341 | PAN,OIL | |||||||||||||||
| C2831342 | PAN,OIL | |||||||||||||||
| C2831370 | HOUSING,FLYWHEEL | |||||||||||||||
| C2834174 | TURBOCHARGER | |||||||||||||||
| C2834176 | TURBOCHARGER | |||||||||||||||
| C2834302 | TURBOCHARGER | |||||||||||||||
| C2834338 | TURBOCHARGER | |||||||||||||||
| C2834535 | TURBOCHARGER | |||||||||||||||
| C2834797 | TURBOCHARGER | |||||||||||||||
| C2834799 | TURBOCHARGER | |||||||||||||||
| C2834823 | TURBOCHARGER | |||||||||||||||
| C2835419 | TURBOCHARGER | |||||||||||||||
| C2835420 | TURBOCHARGER | |||||||||||||||
| C2836276 | TURBOCHARGER | |||||||||||||||
| C2836441 | TURBOCHARGER | |||||||||||||||
| C2836739 | TURBOCHARGER | |||||||||||||||
| C2837154 | TURBOCHARGER | |||||||||||||||
| C2837412 | TURBOCHARGER | |||||||||||||||
| C2838287 | TURBOCHARGER | |||||||||||||||
| C2839128 | TURBOCHARGER | |||||||||||||||
| C2839315 | TURBOCHARGER | |||||||||||||||
| C2839317 | TURBOCHARGER | |||||||||||||||
| C2839319 | TURBOCHARGER | |||||||||||||||
| C2839354 | TURBOCHARGER | |||||||||||||||
| C2839387 | TURBOCHARGER | |||||||||||||||
| C2839487 | TURBOCHARGER | |||||||||||||||
| C2839489 | TURBOCHARGER | |||||||||||||||
| C2839878 | TURBOCHARGER | |||||||||||||||
| C2840195 | TURBOCHARGER | |||||||||||||||
| C2840947 | TURBOCHARGER | |||||||||||||||
| C2841270 | TURBOCHARGER | |||||||||||||||
| C2841384 | TURBOCHARGER | |||||||||||||||
| C2841698 | TURBOCHARGER | |||||||||||||||
| C2842807 | TURBOCHARGER | |||||||||||||||
| C2842849 | TURBOCHARGER | |||||||||||||||
| C2864829 | SEAL,GEAR HOUSING | |||||||||||||||
| C2864882 | HOUSING,GEAR | |||||||||||||||
| C2864884 | SHAFT,IDLER | |||||||||||||||
| C2864886 | GASKET,COVER PLATE | |||||||||||||||
| C2864887 | PLATE,COVER | |||||||||||||||
| C2864899 | SCREW,CONNECTING ROD CAP | |||||||||||||||
| C2866616 | BOSS | |||||||||||||||
| C2869891 | GASKET,VALVE COVER | |||||||||||||||
| C2869892 | GEAR,IDLER | |||||||||||||||
| C2869962 | NOZZLE,PISTON COOLING | |||||||||||||||
| C2870121 | SEAL,FRONT COVER | |||||||||||||||
| C2871979 | SENSOR,NITROGEN OXIHU (WEST LAKE) DIS. | |||||||||||||||
| C2872277 | SENSOR,POSITION | |||||||||||||||
| C2872279 | SENSOR,POSITION | |||||||||||||||
| C2872792 | SENSOR,TEMPERATURE | |||||||||||||||
| C2873953 | BRACKET,LIFTING | |||||||||||||||
| C2873961 | SEAL,O RING | |||||||||||||||
| C2873968 | HOSE,ELBOW | |||||||||||||||
| C2873969 | PULLEY,FAN | |||||||||||||||
| C2873971 | HUB,FAN | |||||||||||||||
| C2873972 | SUPPORT,BELT TENSIONER | |||||||||||||||
| C2873974 | BELT,V RIBBED | |||||||||||||||
| C2873975 | SUPPORT,ALTERNATOR | |||||||||||||||
| C2873982 | GASKET,EXHAUST MANIFOLD | |||||||||||||||
| C2873983 | HOSE,FLEXIBLE | |||||||||||||||
| C2873984 | CONNECTION,TUR OIL DRAIN | |||||||||||||||
| C2873989 | SCREW,FRACTURE RESISTANT | |||||||||||||||
| C2874016 | HEAD,FUEL FILTER | |||||||||||||||
| C2874571 | TENSIONER,BELT | |||||||||||||||
| C2874571 | BELT,V RIBBED | |||||||||||||||
| C2874033 | BRACE,TUBE | |||||||||||||||
| C2874037 | TUBE,WATER BYPASS | |||||||||||||||
| C2874042 | PUMP,WATER | |||||||||||||||
| C2874044 | CARRIER,SEAL | |||||||||||||||
| C2874047 | COUPLING,PLAIN HOSE | |||||||||||||||
| C2874051 | HARNESS,ETR CNT MDL WRG | |||||||||||||||
| C2874066 | BLOCK,CYLINDER | |||||||||||||||
| C2874071 | PULLEY,IDLER | |||||||||||||||
| C2874076 | PLATE,OIL SEAL | |||||||||||||||
| C2874077 | SCREW,HEX FLANGE HEAD CAP | |||||||||||||||
| C2874078 | WASHER,PLAIN | |||||||||||||||
| C2874079 | COVER,GEAR | |||||||||||||||
| C2874091 | SCREW,HEX FLANGE HEAD | |||||||||||||||
| C2874093 | HOUSING,OIL COOLER | |||||||||||||||
| C2874120 | CONNECTION,AIR INTAKE | |||||||||||||||
| C2874205 | CONNECTION,AIR TRANSFER | |||||||||||||||
| C2874278 | PUMP,WATER | |||||||||||||||
| C2874279 | ALTERNATOR | |||||||||||||||
| C2874377 | TENSIONER,BELT | |||||||||||||||
| C2874451 | CONNECTOR,BANJO | |||||||||||||||
| C2874467 | UNION,MALE | |||||||||||||||
| C2874490 | FILTER,LUBRICATING OIL | |||||||||||||||
| C2874557 | CONNECTION,EXHAUST OUTLET | |||||||||||||||
| C2874563 | CONNECTION,AIR TRANSFER | |||||||||||||||
| C2874587 | VALVE,COUPLING | |||||||||||||||
| C2874592 | PUMP,HYDRAULIC | |||||||||||||||
| C2894940 | SENSOR,NITROGEN OXIHU (WEST LAKE) DIS. | |||||||||||||||
| C2897331 | SENSOR,PRESSURE | |||||||||||||||
| C2897333 | SENSOR,PRS TEMPERATURE | |||||||||||||||
| C2897342 | SENSOR,POSITION | |||||||||||||||
| C2897414 | INJECTOR | |||||||||||||||
| C3 | BRACE,TUBE | |||||||||||||||
| C3286494 | PIPE,AIR TRANSFER | |||||||||||||||
| C3286499 | HOSE,PLAIN | |||||||||||||||
| C3286550 | HOSE,PLAIN | |||||||||||||||
| C3286575 | CONNECTION,EXHAUST OUTLET | |||||||||||||||
| C3286613 | SPACER,MOUNTING | |||||||||||||||
| C3286653 | BRACKET,ALTERNATOR | |||||||||||||||
| C3286907 | BRACKET,BELT TENSIONER | |||||||||||||||
| C3286908 | BRACKET,BELT TENSIONER | |||||||||||||||
| C3287571 | SUPPORT,ALTERNATOR | |||||||||||||||
| C3287099 | DIPSTICK | |||||||||||||||
| C3287126 | CONNECTION,EXHAUST OUTLET | |||||||||||||||
| C3287130 | MANIFOLD,EXHAUST | |||||||||||||||
| C3287185 | COUPLING,PLAIN HOSE | |||||||||||||||
| C3287186 | HOSE,MOLDED | |||||||||||||||
| C3287193 | ADAPTER,CRANKSHAFT | |||||||||||||||
| C3287202 | TUBE,CPR WATER INLET | |||||||||||||||
| C3287204 | TUBE,CPR WATER OUTLET | |||||||||||||||
| C3287206 | TUBE,CPR WATER OUTLET | |||||||||||||||
| C3287208 | TUBE,CPR WATER OUTLET | |||||||||||||||
| C3287210 | TUBE,CPR WATER INLET | |||||||||||||||
| C3287272 | CLAMP,HOSE | |||||||||||||||
| C3287273 | CONNECTOR,QCK DISCONNECT | |||||||||||||||
| C3287274 | CONNECTOR,QCK DISCONNECT | |||||||||||||||
| C32873). If you don’t have part no in hand, you can also tell us the engine number (8 Arab numbers, like25262227). CHINAMFG Quickserve on line could help. /* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
Welchen Beitrag leisten Riemenscheiben zum Betrieb von Fördersystemen?Pulleys play a critical role in the operation of conveyor systems by facilitating the movement of materials or products along the conveyor belt. Here’s how pulleys contribute to the functioning of conveyor systems: 1. Kraftübertragung: Fördersysteme verwenden normalerweise eine motorisierte Riemenscheibe, auch Antriebsriemenscheibe oder Kopfriemenscheibe genannt, die mit einem Elektromotor verbunden ist. Der Motor dreht die Antriebsriemenscheibe, die wiederum das Förderband bewegt. Die Drehkraft des Motors wird über die Antriebsriemenscheibe auf das Band übertragen, wodurch die kontinuierliche Bewegung des Bandes und der beförderten Materialien ermöglicht wird. 2. Bandspannung und -führung: Riemenscheiben werden verwendet, um die richtige Spannung im Förderband aufrechtzuerhalten. Spannrollen, auch Umlenkrollen genannt, werden strategisch entlang des Fördersystems platziert, um Spannung auf das Band auszuüben. Diese Rollen helfen, das Band straff zu halten und ein Verrutschen oder Durchhängen zu verhindern. Darüber hinaus werden Führungsrollen verwendet, um das Förderband auszurichten und sicherzustellen, dass es zentriert bleibt und reibungslos entlang der vorgesehenen Bahn läuft. 3. Lastunterstützung: Riemenscheiben stützen das Förderband und die von ihm getragene Last. Das Band wickelt sich um die Riemenscheiben und die Last wird über die Oberfläche des Bandes verteilt. Riemenscheiben mit größeren Durchmessern werden häufig an Stellen verwendet, an denen schwere Lasten auftreten, um die Last effektiver zu verteilen und Verformungen oder Schäden am Band zu verhindern. 4. Richtungsänderungen: Fördersysteme können Richtungsänderungen erfordern, um dem Layout oder spezifischen Verarbeitungsanforderungen gerecht zu werden. Umlenkrollen, auch als Umlenkrollen oder Einschnürrollen bekannt, werden verwendet, um das Band umzulenken und seinen Lauf zu ändern. Diese Rollen sind so konzipiert, dass sie das Band reibungslos um Biegungen oder Ecken führen, ohne das Band übermäßig zu belasten. 5. Geschwindigkeitsregelung: Riemenscheiben können zur Geschwindigkeitsregelung in Fördersystemen eingesetzt werden. Durch die Verwendung von Riemenscheiben unterschiedlicher Größe oder durch den Einsatz von Antrieben mit variabler Geschwindigkeit kann die Drehzahl der Antriebsriemenscheibe angepasst werden, wodurch die Geschwindigkeit beeinflusst wird, mit der sich das Förderband bewegt. Dies ermöglicht Flexibilität im Förderprozess und ermöglicht die Anpassung an unterschiedliche Materialflussraten oder spezifische Betriebsanforderungen. 6. Systemunterstützung und Stabilität: Riemenscheiben und die dazugehörigen Stützstrukturen sorgen für Stabilität im Fördersystem. Sie helfen, die Ausrichtung und Spannung des Bandes aufrechtzuerhalten und verhindern Fehlausrichtungen, Vibrationen und übermäßige Bandbewegungen. Richtig konstruierte und gewartete Riemenscheiben tragen zur allgemeinen Zuverlässigkeit und zum reibungslosen Betrieb des Fördersystems bei. Fördersysteme werden häufig in Branchen wie Fertigung, Bergbau, Logistik und Lagerhaltung eingesetzt. Riemenscheiben sind wichtige Komponenten, die die effiziente und zuverlässige Bewegung von Materialien und Produkten entlang des Förderbands gewährleisten und automatisierte und kontinuierliche Materialhandhabungsprozesse ermöglichen.
Können Flaschenzüge sowohl zum horizontalen als auch zum vertikalen Heben verwendet werden?Yes, pulleys can be used for both horizontal and vertical lifting. The versatility of pulley systems allows them to be utilized in various lifting applications, regardless of the direction of the load. Here’s how pulleys can be used for horizontal and vertical lifting: 1. Horizontales Heben: Beim horizontalen Heben können Seilrollen eingesetzt werden, um die Richtung der auf die Last ausgeübten Kraft zu ändern. Durch die Verwendung einer Kombination aus festen und beweglichen Seilrollen kann die Kraft umgeleitet werden, um die Last horizontal zu ziehen. Dies ist häufig bei Anwendungen wie manuellen Hebezeugen oder Flaschenzugsystemen im Bauwesen zu beobachten, bei denen schwere Objekte horizontal über Entfernungen bewegt werden müssen. 2. Vertical Lifting: Pulleys are widely used in vertical lifting applications, such as cranes, elevators, and lifting systems. In these setups, the pulleys are typically arranged in such a way that the load can be lifted vertically. By using multiple pulleys and ropes or cables, mechanical advantage can be achieved, making lifting heavier loads easier. The pulleys distribute the load’s weight across multiple lines, reducing the effort required to lift the load. It’s worth noting that the number and arrangement of pulleys can vary depending on the specific lifting requirements. For example, a single fixed pulley can change the direction of the force but does not provide any mechanical advantage. On the other hand, systems with multiple pulleys, such as compound pulley systems or block and tackle setups, can provide significant mechanical advantage, making lifting heavier loads more manageable. Ob horizontales oder vertikales Heben, die Prinzipien der Flaschenzugmechanik bleiben dieselben. Flaschenzüge ermöglichen Kraftumleitung, mechanische Kraftübertragung und Lastverteilung, wodurch Hebeaufgaben effizienter und handhabbarer werden. Die spezifische Konfiguration und Einrichtung des Flaschenzugsystems hängt von den Hebeanforderungen und dem gewünschten Grad an mechanischer Kraftübertragung ab.
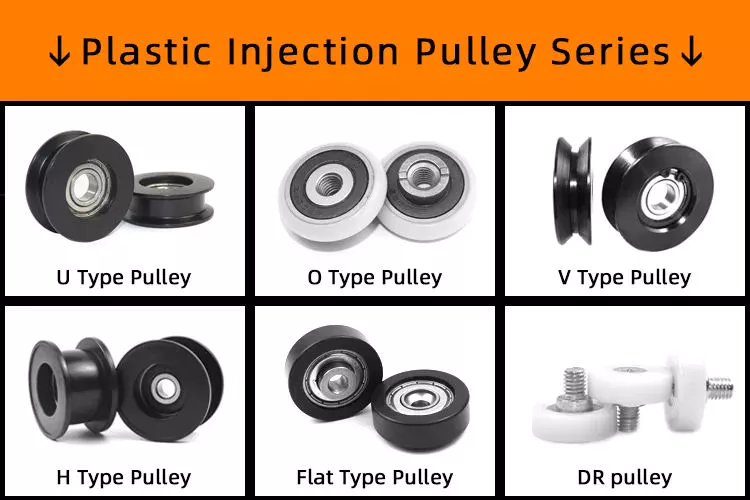
What materials are typically used to manufacture pulleys?Pulleys are manufactured using a variety of materials, depending on the specific application and requirements. Here are some of the materials that are typically used to manufacture pulleys: 1. Metal Alloys: Metal alloys such as steel and cast iron are commonly used to manufacture pulleys. Steel pulleys offer excellent strength, durability, and resistance to wear and corrosion. Cast iron pulleys are known for their high strength and resistance to impact and shock loads. Metal alloys are preferred in heavy-duty applications where strength and durability are critical. 2. Aluminum: Aluminum is widely used in pulley manufacturing due to its lightweight nature and corrosion resistance. Aluminum pulleys are commonly used in applications that require reduced weight, such as automotive engines, aircraft components, and light-duty machinery. They offer good strength-to-weight ratio and are suitable for applications where weight reduction is a priority. 3. Plastic: Various types of plastics, including nylon, polyurethane, and high-density polyethylene (HDPE), are used to manufacture pulleys. Plastic pulleys are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and offer good resistance to wear and abrasion. They are commonly used in applications where noise reduction, chemical resistance, or non-conductive properties are required. Plastic pulleys are frequently used in conveyor systems, packaging machinery, and small-scale equipment. 4. Composite Materials: Composite materials, such as fiberglass-reinforced plastic (FRP) and carbon fiber-reinforced polymer (CFRP), are utilized in the manufacturing of pulleys. These materials offer high strength-to-weight ratios, excellent resistance to corrosion, and good fatigue resistance. Composite pulleys are commonly used in industries such as aerospace, marine, and sports equipment, where lightweight components with exceptional strength are required. 5. Ceramics: In certain specialized applications, pulleys made of ceramics like aluminum oxide (alumina) or silicon nitride are used. Ceramic pulleys offer exceptional hardness, high temperature resistance, and excellent wear resistance. They are primarily used in industries such as semiconductor manufacturing, where extreme precision, chemical resistance, and resistance to high temperatures are crucial. It’s important to note that the choice of material for pulley manufacturing depends on factors such as load capacity, operating conditions, environmental factors, and cost considerations. Manufacturers select materials that provide the necessary properties to meet the specific requirements of the application while considering factors such as strength, durability, weight, and cost.
2023-12-21 Verwandte Artikel |