Produktbeschreibung
Product Description:
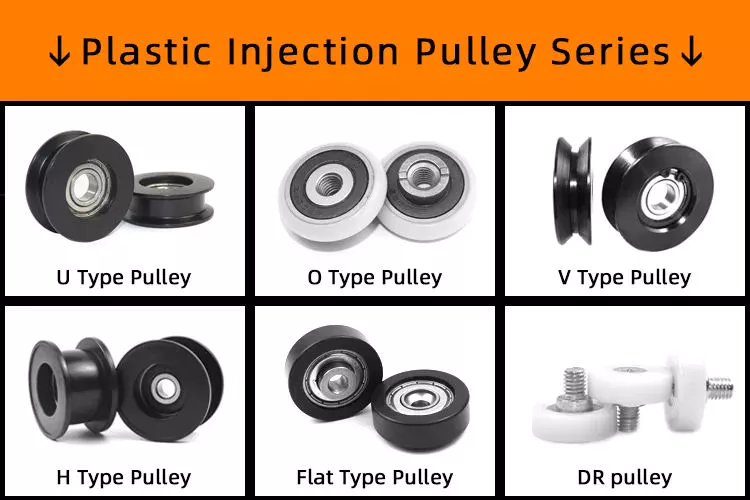
Product Name: Sliding Roller HN-1035-9
Dimensions: ID=10mm; OD=35mm; Height=9mm
Outside Material: Polyformaldehyde (POM), Polyamide(PA6, PA66, Nylon), Polypropylene(PP), Polycarbonate(PC), Polyurethane(PU)
Insert Material: Carbon Steel, Chrome Steel, Stainless Steel
Color: All colors available
Profile Type:V Groove
Surface Treatment: Lathing
Structure: HN-625ZZ(ID=10mm, OD=35mm, Width=9mm)bearing injected with POM
Service: OEM&ODM
Experience: With 15 years manufacturing history
Adventage:
1) Built-in precise micro bearing;
2) Low noise, elegant performance and rolling smoothly;
3) Superior in quality and moderate in price;
4) We can supply both standard products and customized items according to the customers’ special requirements.
5) We can provide free samples for your reference.
Payment & Packaging &Delivery:
Payment Terms:
1) 100% T/T
2) 30% T/T in advance, 70% against copy of BL
3) Paypal
Packaging Details: Standard export packing (Plastic bag, cartons and pallets or wooden case);
As customers’ requirement
Delivery Port: HangZhou / ZheJiang
Delivery Time: Normally ready goods and stock within 30 days or as the customer’s request
PS: 1) material and color can according to customers’ requirement.
2) we can make different size as per customers’ requirement.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Q: Are you the manufacturer?
A: Yes, we are a professional manufacturer focused on door and window roller pulleys for over 15 years.
Q: Do you offer free samples?
A: Yes, we are very glad to offer free samples for you to check the quality.
Q: Can we make our own color box?
A: Yes, if the order quantity reaches 1000 sets, we can make a customized color box for you.
Q: Can we print our logo on the products?
A: Yes, we can print your logo on the products according to your design.
Q: How does your factory do regarding quality control?
A: 80% of the staff has 10 years experience, a mature skilled technical team, and a complete quality management system to ensure high quality.
Q: What is the after-sale service for the sliding rollers?
A: We have online technical support. If it is a quality problem, we will replace the broken ones with new ones.
Q: How long is the production time?
A: For samples in stock, shipped in 2 days. if not in stock, the lead time is in 7 days. For mass production, the lead time is around 15 days after receiving the deposit payment.
Q: How about the shipment?
A: For small orders, we can ship them by DHL, FedEx, UPS, TNT, etc. For mass production orders, we can ship them by sea or by air. /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Contact Angle: | / |
|---|---|
| Aligning: | Bearing |
| Separated: | Unseparated |
| Load Direction: | Radial Bearing |
| Material: | Nylon/Plastic/POM |
| Features: | Work Smoothly,Low Noise,Widely Use,Standard,Custo |
| Proben: |
US$ 0/Piece
1 Stück (Mindestbestellmenge) | |
|---|
| Anpassung: |
Verfügbar
| Kundenspezifische Anfrage |
|---|

What are the common problems and maintenance requirements for pulleys?
Pulleys, like any mechanical component, can experience common problems and require regular maintenance to ensure their proper functioning and longevity. Here are some of the common problems and maintenance requirements for pulleys:
1. Wear and Tear: Over time, pulleys can experience wear and tear due to friction, load stress, and environmental factors. This can result in issues such as worn grooves, cracked or deformed pulley bodies, or damaged bearings. Regular inspection is necessary to identify signs of wear and address them promptly.
2. Misalignment: Pulleys can become misaligned, causing the belt or rope to run off its intended path. This can lead to inefficient power transmission, increased wear on the belt, and reduced overall system performance. Regular alignment checks and adjustments are necessary to ensure proper alignment of pulleys and belts.
3. Belt Tension: Proper belt tension is crucial for optimal pulley performance. Over time, belts can stretch or become loose, resulting in inadequate tension. Insufficient tension can cause slippage, reduced power transfer, and premature wear. Regular checks and adjustments of belt tension are necessary to maintain optimal performance.
4. Contamination: Pulleys can accumulate dirt, dust, debris, or other contaminants, particularly in industrial or outdoor environments. Contamination can lead to increased friction, reduced efficiency, and accelerated wear. Regular cleaning of pulleys is necessary to prevent buildup and maintain smooth operation.
5. Lubrication: Pulleys with bearings require proper lubrication to minimize friction and ensure smooth rotation. Insufficient lubrication can lead to increased friction, heat generation, and premature bearing failure. Regular lubrication according to manufacturer recommendations is essential for optimal pulley performance and longevity.
6. Bearing Maintenance: Pulleys with bearings should undergo regular bearing maintenance. This includes inspecting bearings for signs of wear or damage, cleaning them, and replacing worn-out or faulty bearings. Proper bearing maintenance helps prevent bearing failure, which can lead to pulley malfunction or system downtime.
7. Environmental Factors: Pulleys used in outdoor or harsh environments may be exposed to adverse conditions such as extreme temperatures, moisture, chemicals, or corrosive substances. Extra care should be taken to protect pulleys from these environmental factors. This may involve using appropriate seals, covers, or coatings and implementing preventive measures to mitigate the effects of the environment.
8. Regular Inspections: Regular inspections are crucial for identifying potential problems early on. Inspect pulleys for signs of wear, damage, misalignment, or other issues. Address any identified problems promptly to prevent further damage or system failure.
9. Replacement of Worn-out Parts: If any components of the pulley, such as the belt, bearings, or fasteners, are worn out or damaged beyond repair, they should be replaced promptly. Using worn-out parts can compromise the performance and safety of the pulley system.
10. Manufacturer Guidelines: Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for maintenance and servicing of pulleys. Manufacturers often provide specific instructions on maintenance intervals, lubrication requirements, and other important considerations.
By proactively addressing these common problems and adhering to regular maintenance requirements, pulley performance and service life can be optimized, ensuring smooth and reliable operation in various applications.
Können Flaschenzüge sowohl zum horizontalen als auch zum vertikalen Heben verwendet werden?
Yes, pulleys can be used for both horizontal and vertical lifting. The versatility of pulley systems allows them to be utilized in various lifting applications, regardless of the direction of the load. Here’s how pulleys can be used for horizontal and vertical lifting:
1. Horizontales Heben: Beim horizontalen Heben können Seilrollen eingesetzt werden, um die Richtung der auf die Last ausgeübten Kraft zu ändern. Durch die Verwendung einer Kombination aus festen und beweglichen Seilrollen kann die Kraft umgeleitet werden, um die Last horizontal zu ziehen. Dies ist häufig bei Anwendungen wie manuellen Hebezeugen oder Flaschenzugsystemen im Bauwesen zu beobachten, bei denen schwere Objekte horizontal über Entfernungen bewegt werden müssen.
2. Vertical Lifting: Pulleys are widely used in vertical lifting applications, such as cranes, elevators, and lifting systems. In these setups, the pulleys are typically arranged in such a way that the load can be lifted vertically. By using multiple pulleys and ropes or cables, mechanical advantage can be achieved, making lifting heavier loads easier. The pulleys distribute the load’s weight across multiple lines, reducing the effort required to lift the load.
It’s worth noting that the number and arrangement of pulleys can vary depending on the specific lifting requirements. For example, a single fixed pulley can change the direction of the force but does not provide any mechanical advantage. On the other hand, systems with multiple pulleys, such as compound pulley systems or block and tackle setups, can provide significant mechanical advantage, making lifting heavier loads more manageable.
Ob horizontales oder vertikales Heben, die Prinzipien der Flaschenzugmechanik bleiben dieselben. Flaschenzüge ermöglichen Kraftumleitung, mechanische Kraftübertragung und Lastverteilung, wodurch Hebeaufgaben effizienter und handhabbarer werden. Die spezifische Konfiguration und Einrichtung des Flaschenzugsystems hängt von den Hebeanforderungen und dem gewünschten Grad an mechanischer Kraftübertragung ab.
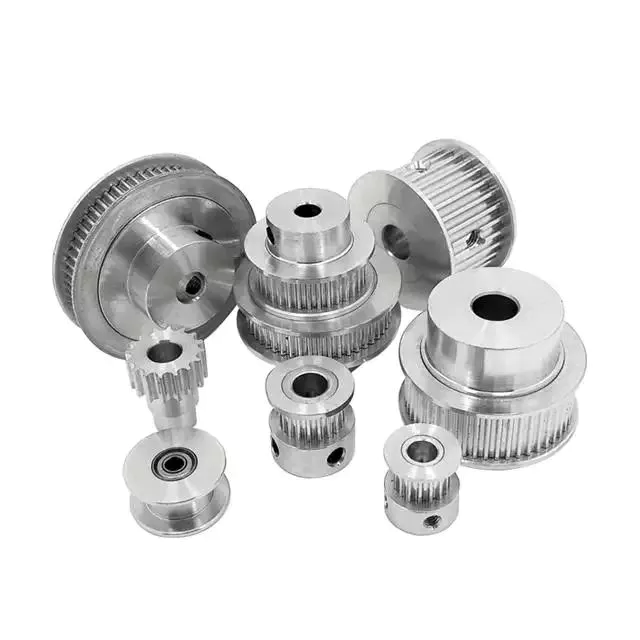

Welche unterschiedlichen Arten von Riemenscheiben werden in der Industrie üblicherweise verwendet?
Riemenscheiben werden in verschiedenen Branchen für unterschiedliche Anwendungen eingesetzt. Hier sind die verschiedenen Arten von Riemenscheiben, die häufig verwendet werden:
1. Feste Rollen: Feste Rollen sind an einer stationären Struktur wie einer Decke oder Wand befestigt. Sie ändern die Richtung der angewandten Kraft, ohne einen mechanischen Vorteil zu bieten. Feste Rollen werden oft in Kombination mit anderen Rollen verwendet, um komplexere Systeme zu schaffen.
2. Bewegliche Rollen: Bewegliche Rollen sind an der zu bewegenden Last befestigt und bewegen sich mit ihr. Diese Rollen bieten einen mechanischen Vorteil, indem sie den zum Anheben der Last erforderlichen Kraftaufwand verringern. Bewegliche Rollen werden häufig in Systemen wie Flaschenzügen verwendet, um schwere Objekte mit weniger Kraft anzuheben.
3. Verbundrollen: Verbundrollen bestehen aus einer Kombination von festen und beweglichen Rollen. Sie bieten einen größeren mechanischen Vorteil als eine einzelne Rolle, indem sie die Last auf mehrere Segmente des Seils oder Riemens verteilen. Verbundrollensysteme werden häufig in Anwendungen eingesetzt, bei denen extrem schwere Lasten gehoben werden müssen.
4. Umlenkrollen: Umlenkrollen sind Rollen mit einer Seitenplatte, die geöffnet werden kann, um ein Seil oder Kabel einzuführen oder zu entfernen, ohne es durch die Rolle zu fädeln. Sie werden häufig in Takelage- und Schleppanwendungen verwendet, um die Kraftrichtung zu ändern und einen mechanischen Vorteil zu erzielen.
5. Keilriemenscheiben: Keilriemenscheiben haben eine V-förmige Nut, die dem Querschnitt von Keilriemen entspricht. Sie werden in Riemenantriebssystemen verwendet, um Kraft zwischen zwei Wellen zu übertragen. Keilriemenscheiben werden häufig in Anwendungen wie Industriemaschinen, Automotoren und HLK-Systemen eingesetzt.
6. Zahnriemenscheiben: Zahnriemenscheiben haben Zähne, die in die Zähne eines Zahnriemens greifen. Sie werden in synchronen Antriebssystemen verwendet, um eine genaue und synchronisierte Kraftübertragung zu gewährleisten. Zahnriemenscheiben werden häufig in Anwendungen wie Robotern, Druckmaschinen und CNC-Maschinen verwendet.
7. Seilrollen: Seilrollen haben eine glatte Oberfläche, die Reibung minimiert und Seilverschleiß verhindert. Sie werden häufig in Anwendungen eingesetzt, in denen Seile zum Heben oder Ziehen verwendet werden, wie z. B. bei Kränen, Aufzügen und Materialtransportgeräten.
8. Drahtseilrollen: Drahtseilrollen sind speziell für die Verwendung mit Drahtseilen konzipiert. Sie haben Rillen oder Taschen, die sich der Form und Größe von Drahtseilen anpassen und so sicheren Halt und effiziente Kraftübertragung gewährleisten. Drahtseilrollen werden häufig in Anwendungen wie Kränen, Winden und Hebezeugen eingesetzt.
9. Umlenkrollen: Umlenkrollen werden verwendet, um Riemen oder Seile in einem System zu führen und zu spannen. Sie übertragen keine Kraft, helfen aber dabei, die richtige Riemenspannung und -ausrichtung aufrechtzuerhalten. Umlenkrollen werden häufig in Fördersystemen, Automotoren und anderen riemengetriebenen Anwendungen verwendet.
10. Seilscheiben: Seilscheiben sind große Seilscheiben, die in Schwerlastanwendungen wie Kransystemen und Aufzügen eingesetzt werden. Sie sind für hohe Belastungen ausgelegt und sorgen für einen reibungslosen und zuverlässigen Betrieb. Seilscheiben haben oft mehrere Rillen, um mehrere Seile oder Riemen aufzunehmen.
Dies sind einige der verschiedenen Riemenscheibentypen, die häufig in verschiedenen Branchen verwendet werden. Jeder Typ hat spezifische Merkmale und wird basierend auf den Anforderungen der Anwendung ausgewählt, wie z. B. Tragfähigkeit, Kraftübertragung und Betriebsbedingungen.


Herausgeber von CX
2024-03-14
